- 1.
Alberti KGM, Zimmet P, Shaw J. The metabolic syndrome—a new worldwide definition. Lancet. 2005;366(9491):1059–62.
Article Google Scholar
- 2.
Ebrahimpour P, Fakhrzadeh H, Heshmat R, Ghodsi M, Bandarian F, Larijani B. Metabolic syndrome and menopause: a population-based study. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2010;4(1):5–9.
Article Google Scholar
- 3.
Shiwaku K, Nogi A, Kitajima K, Anuurad E, Enkhmaa B, Yamasaki M, et al. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome using the modified ATP III definitions for workers in Japan, Korea and Mongolia. J Occup Health. 2005;47(2):126–35.
Article Google Scholar
- 4.
Freiberger E, Häberle L, Spirduso WW, Rixt Zijlstra G. Long-term effects of three multicomponent exercise interventions on physical performance and fall-related psychological outcomes in community-dwelling older adults: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60(3):437–46.
Article Google Scholar
- 5.
Small DM, Coombes JS, Bennett N, Johnson DW, Gobe GC. Oxidative stress, anti-oxidant therapies and chronic kidney disease. Nephrology. 2012;17(4):311–21.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 6.
Spradley BD, Crowley KR, Tai C-Y, Kendall KL, Fukuda DH, Esposito EN, et al. Ingesting a pre-workout supplement containing caffeine, B-vitamins, amino acids, creatine, and beta-alanine before exercise delays fatigue while improving reaction time and muscular endurance. Nutr Metab. 2012;9(1):28.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 7.
Wagner CL, McNeil R, Hamilton SA, Winkler J, Cook CR, Warner G, et al. A randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation in 2 community health center networks in South Carolina. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;208(2):137.
Article Google Scholar
- 8.
Fedirko V, Bostick RM, Long Q, Flanders WD, McCullough ML, Sidelnikov E, et al. Effects of supplemental vitamin D and calcium on oxidative DNA damage marker in normal colorectal mucosa: a randomized clinical trial. Cancer Epidemiol Prev Biomark. 2010;19(1):280–91.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 9.
Mithal A, Bonjour J-P, Boonen S, Burckhardt P, Degens H, Fuleihan GEH, et al. Impact of nutrition on muscle mass, strength, and performance in older adults. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(5):1555–66.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 10.
Myburgh KH. Polyphenol supplementation: benefits for exercise performance or oxidative stress? Sports Med. 2014;44(1):57–70.
Article Google Scholar
- 11.
Chowdhury R, Kunutsor S, Vitezova A, Oliver-Williams C, Chowdhury S, Kiefte-de-Jong JC, et al. Vitamin D and risk of cause specific death: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational cohort and randomised intervention studies. BMJ. 2014;348:g1903.
Article Google Scholar
- 12.
Grandi NC, Breitling LP, Brenner H. Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Prev Med. 2010;51(3–4):228–33.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 13.
Scott D, Blizzard L, Fell J, Ding C, Winzenberg T, Jones G. A prospective study of the associations between 25-hydroxy-vitamin D, sarcopenia progression and physical activity in older adults. Clin Endocrinol. 2010;73(5):581–7.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 14.
Beaudart C, Buckinx F, Rabenda V, Gillain S, Cavalier E, Slomian J, et al. The effects of vitamin D on skeletal muscle strength, muscle mass, and muscle power: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(11):4336–45.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 15.
Pludowski P, Holick MF, Pilz S, Wagner CL, Hollis BW, Grant WB, et al. Vitamin D effects on musculoskeletal health, immunity, autoimmunity, cardiovascular disease, cancer, fertility, pregnancy, dementia and mortality—a review of recent evidence. Autoimmun Rev. 2013;12(10):976–89.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 16.
Stockton K, Mengersen K, Paratz J, Kandiah D, Bennell K. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on muscle strength: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(3):859–71.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
- 17.
Paknahad Z, Vasmehjani AA, Maracy MR. Association of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin d levels with markers of metabolic syndrome in adult women in Ramsar, Iran. Women's Health Bull. 2014;1(1):e20124.
Article Google Scholar
- 18.
Saneei P, Salehi-Abargouei A, Esmaillzadeh A. Serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels in relation to body mass index: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2013;14(5):393–404.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 19.
Anstey K, Cherbuin N, Budge M, Young J. Body mass index in midlife and late-life as a risk factor for dementia: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Obes Rev. 2011;12(5):e426–37.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 20.
Gonzalez AB, Hartge P, Cerhan JR, Flint AJ, Hannan L, MacInnis RJ, et al. Body-mass index and mortality among 1.46 million white adults. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(23):2211–9.
Article Google Scholar
- 21.
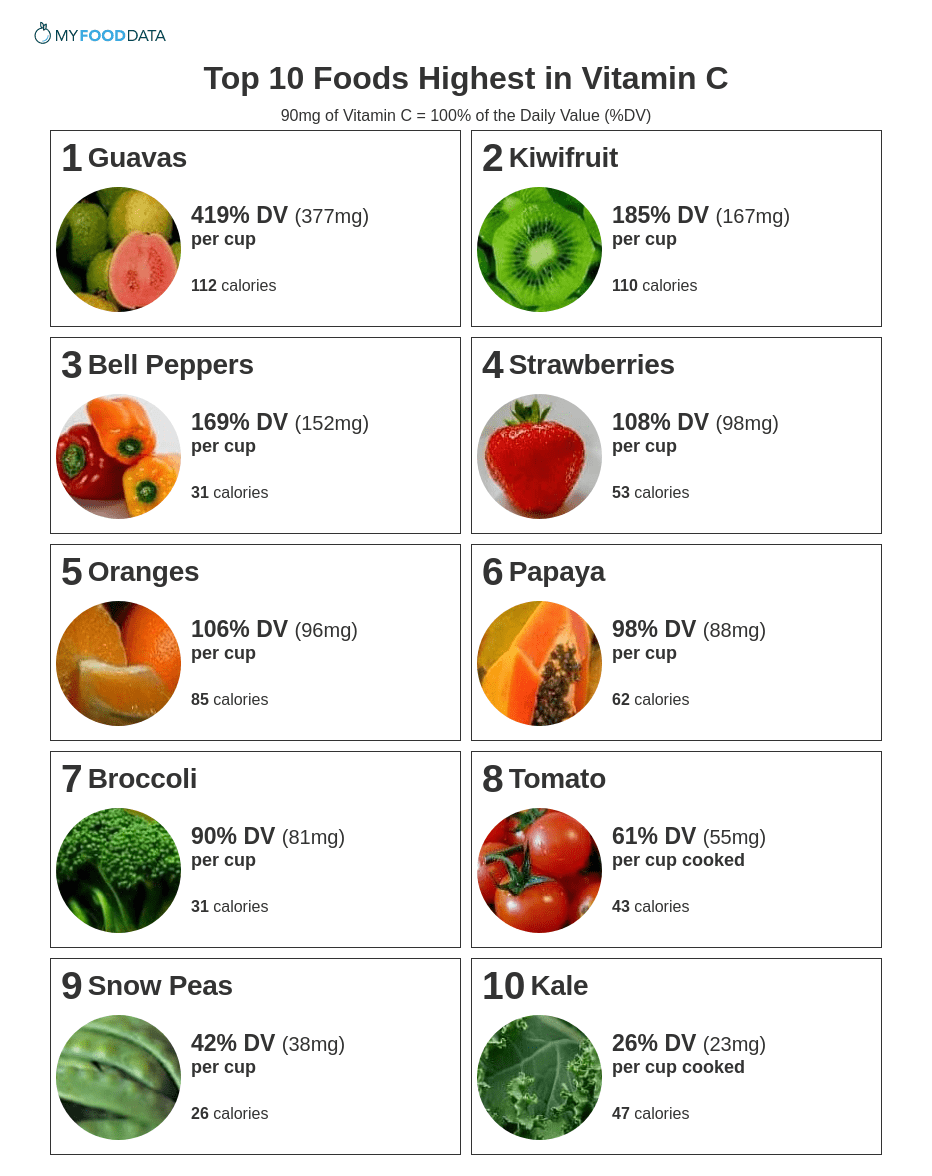
Ramful D, Tarnus E, Aruoma OI, Bourdon E, Bahorun T. Polyphenol composition, vitamin C content and antioxidant capacity of Mauritian citrus fruit pulps. Food Res Int. 2011;44(7):2088–99.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 22.
Jun S, Jung E, Kang D, Kim J, Chang U, Suh HJ. Vitamin C increases the fecal fat excretion by chitosan in guinea-pigs, thereby reducing body weight gain. Phytother Res. 2010;24(8):1234–41.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
- 23.
Asemi Z, Zare Z, Shakeri H, Sabihi S-S, Esmaillzadeh A. Effect of multispecies probiotic supplements on metabolic profiles, hs-CRP, and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes. Ann Nutr Metab. 2013;63(1–2):1–9.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 24.
Barbieri E, Sestili P. Reactive oxygen species in skeletal muscle signaling. J Sign Transduct. 2012;2012:982794.
Google Scholar
- 25.
Gomes EC, Silva AN, Oliveira MR. Oxidants, antioxidants, and the beneficial roles of exercise-induced production of reactive species. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012;2012:756132.
Article Google Scholar
- 26.
Milić S, Štimac D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/steatohepatitis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation and treatment. Dig Dis. 2012;30(2):158–62.
Article Google Scholar
- 27.
Strasser B. Physical activity in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013;1281(1):141–59.
Article Google Scholar
- 28.
Turi BC, Codogno JS, Fernandes RA, Monteiro HL. Low levels of physical activity and metabolic syndrome: cross-sectional study in the Brazilian public health system. Cien Saude Colet. 2016;21:1043–50.
Article Google Scholar
- 29.
Golder S, Loke YK, Bland M. Meta-analyses of adverse effects data derived from randomised controlled trials as compared to observational studies: methodological overview. PLoS Med. 2011;8(5):e1001026.
Article Google Scholar
- 30.
Stuart EA. Matching methods for causal inference: a review and a look forward. Stat Sci. 2010;25(1):1.
Article Google Scholar
- 31.
Kaftan AN, Hussain MK. Association of adiponectin gene polymorphism rs266729 with type two diabetes mellitus in Iraqi population. A pilot study. Gene. 2015;570(1):95–9.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 32.
Aalto A-M, Elovainio M, Kivimäki M, Uutela A, Pirkola S. The Beck Depression Inventory and General Health Questionnaire as measures of depression in the general population: a validation study using the composite international diagnostic interview as the gold standard. Psychiatry Res. 2012;197(1–2):163–71.
Article Google Scholar
- 33.
De Blacam C, Ogunleye AA, Momoh AO, Colakoglu S, Tobias AM, Sharma R, et al. High body mass index and smoking predict morbidity in breast cancer surgery: a multivariate analysis of 26,988 patients from the national surgical quality improvement program database. Ann Surg. 2012;255(3):551–5.
Article Google Scholar
- 34.
Bull SM. Evidence-based blood conservation education for ICU Nurses: a pre and post-test evaluation of nursing knowledge. 2014. https://uknowledge.uky.edu/dnp_etds/24/.
- 35.
Barzin M, Hosseinpanah F, Fekri S, Azizi F. Predictive value of body mass index and waist circumference for metabolic syndrome in 6–12-year-olds. Acta Paediatr. 2011;100(5):722–7.
Article Google Scholar
- 36.
Rothwell PM, Wilson M, Elwin C-E, Norrving B, Algra A, Warlow CP, et al. Long-term effect of aspirin on colorectal cancer incidence and mortality: 20-year follow-up of five randomised trials. Lancet. 2010;376(9754):1741–50.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 37.
Bauer JM, Verlaan S, Bautmans I, Brandt K, Donini LM, Maggio M, et al. Effects of a vitamin D and leucine-enriched whey protein nutritional supplement on measures of sarcopenia in older adults, the PROVIDE study: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2015;16(9):740–7.
Article Google Scholar
- 38.
Tang BM, Eslick GD, Nowson C, Smith C, Bensoussan A. Use of calcium or calcium in combination with vitamin D supplementation to prevent fractures and bone loss in people aged 50 years and older: a meta-analysis. Lancet. 2007;370(9588):657–66.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 39.
Ginde AA, Liu MC, Camargo CA. Demographic differences and trends of vitamin D insufficiency in the US population, 1988–2004. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169(6):626–32.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 40.
Wolf M, Shah A, Gutierrez O, Ankers E, Monroy M, Tamez H, et al. Vitamin D levels and early mortality among incident hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2007;72(8):1004–13.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 41.
Caan B, Neuhouser M, Aragaki A, Lewis CB, Jackson R, LeBoff MS, et al. Calcium plus vitamin D supplementation and the risk of postmenopausal weight gain. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(9):893–902.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 42.
Zittermann A, Frisch S, Berthold HK, Götting C, Kuhn J, Kleesiek K, et al. Vitamin D supplementation enhances the beneficial effects of weight loss on cardiovascular disease risk markers. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;89(5):1321–7.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 43.
Rosenblum JL, Castro VM, Moore CE, Kaplan LM. Calcium and vitamin D supplementation is associated with decreased abdominal visceral adipose tissue in overweight and obese adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;95(1):101–8.
Article Google Scholar
- 44.
Salehpour A, Hosseinpanah F, Shidfar F, Vafa M, Razaghi M, Dehghani S, et al. A 12-week double-blind randomized clinical trial of vitamin D 3 supplementation on body fat mass in healthy overweight and obese women. Nutr J. 2012;11(1):78.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 45.
Vimaleswaran KS, Berry DJ, Lu C, Tikkanen E, Pilz S, Hiraki LT, et al. Causal relationship between obesity and vitamin D status: bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis of multiple cohorts. PLoS Med. 2013;10(2):e1001383.
Article Google Scholar
- 46.
Amrein K, Sourij H, Wagner G, Holl A, Pieber TR, Smolle KH, et al. Short-term effects of high-dose oral vitamin D3 in critically ill vitamin D deficient patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Crit Care. 2011;15(2):R104.
Article Google Scholar
- 47.
Romaguera D, Ängquist L, Du H, Jakobsen MU, Forouhi NG, Halkjær J, et al. Food composition of the diet in relation to changes in waist circumference adjusted for body mass index. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(8):e23384.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 48.
Du H, van der A DL, Boshuizen HC, Forouhi NG, Wareham NJ, Halkjaer J, et al. Dietary fiber and subsequent changes in body weight and waist circumference in European men and women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;91(2):329–36.
Article Google Scholar
- 49.
Skaaby T, Husemoen LLN, Pisinger C, Jørgensen T, Thuesen BH, Fenger M, et al. Vitamin D status and changes in cardiovascular risk factors: a prospective study of a general population. Cardiology. 2012;123(1):62–70.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- 50.
Wu SH, Ho SC, Zhong L. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on blood pressure. South Med J. 2010;103(8):729–37.
Article Google Scholar
- 51.
Beveridge LA, Struthers AD, Khan F, Jorde R, Scragg R, Macdonald HM, et al. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis incorporating individual patient data. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175(5):745–54.
Article Google Scholar
- 52.
Pittas AG, Chung M, Trikalinos T, Mitri J, Brendel M, Patel K, et al. Systematic review: vitamin D and cardiometabolic outcomes. Ann Intern Med. 2010;152(5):307–14.
Article Google Scholar
- 53.
Dakhale GN, Chaudhari HV, Shrivastava M. Supplementation of vitamin C reduces blood glucose and improves glycosylated hemoglobin in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double-blind study. Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2011;2011:195271.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
- 54.
Berge K, Musa-Veloso K, Harwood M, Hoem N, Burri L. Krill oil supplementation lowers serum triglycerides without increasing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in adults with borderline high or high triglyceride levels. Nutr Res. 2014;34(2):126–33.
CAS Article Google Scholar












 Next ➞
Next ➞